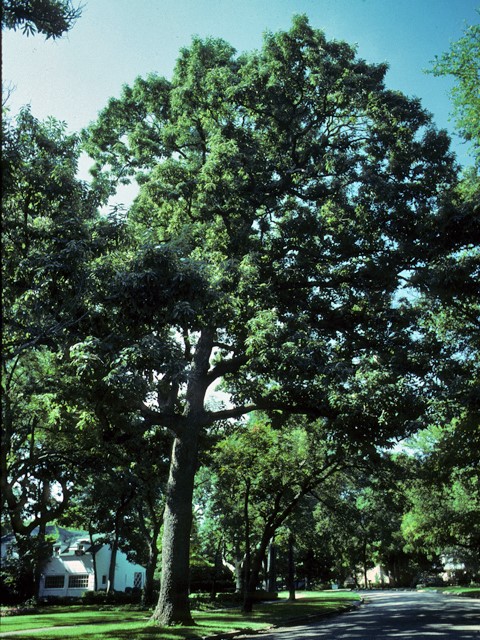
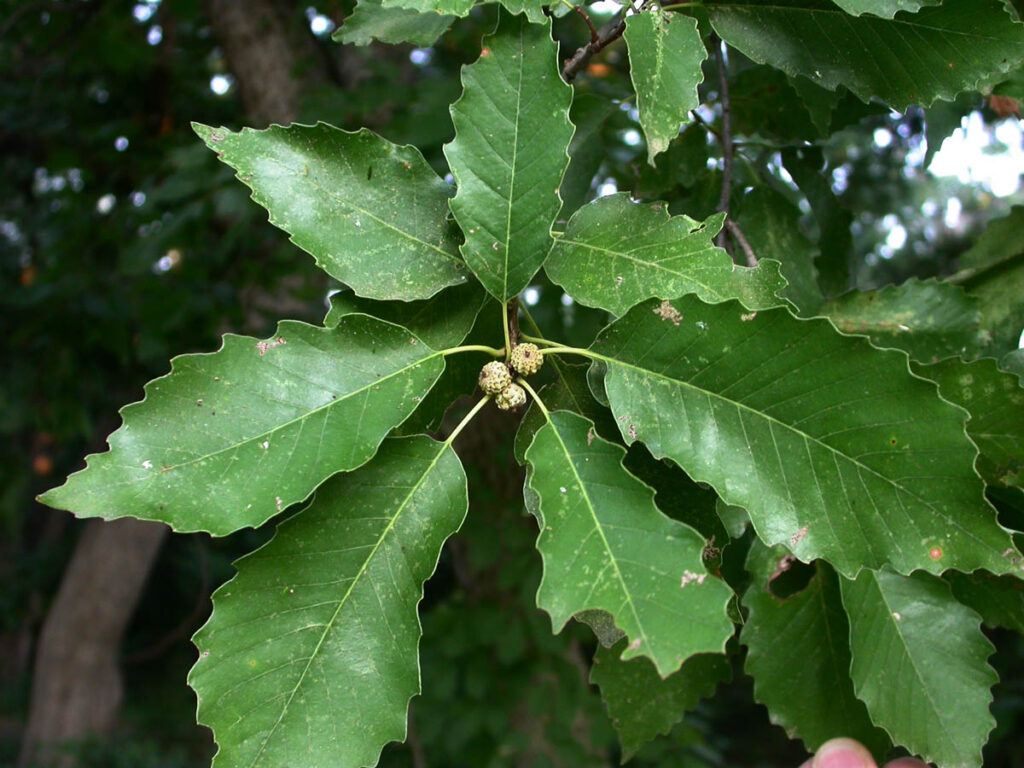
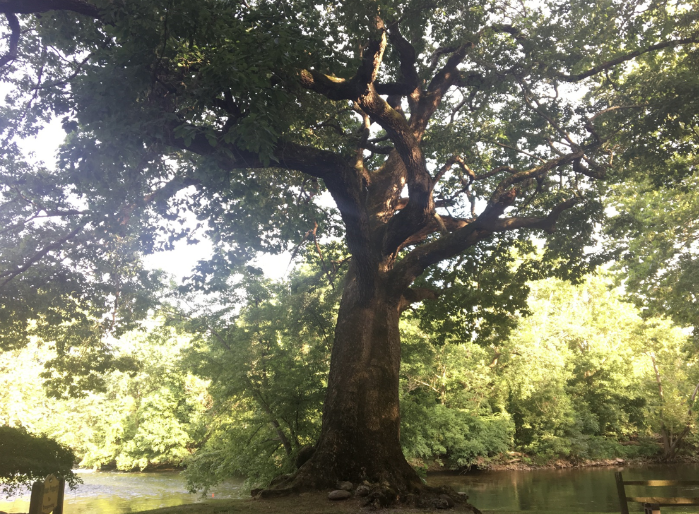
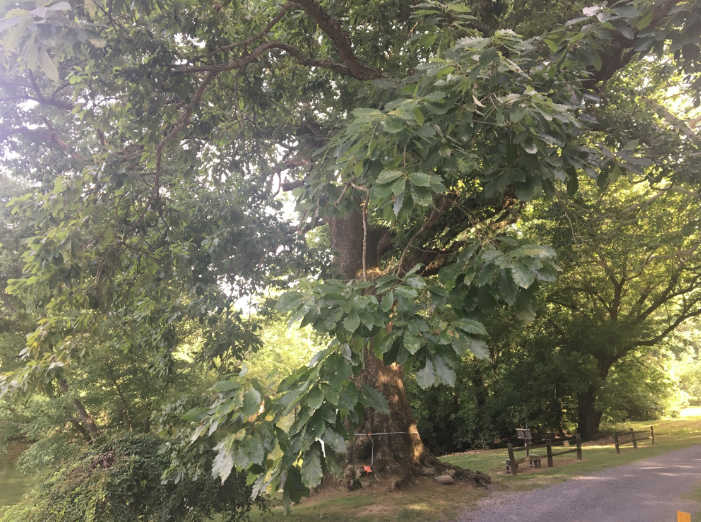
Fun Facts about the Chinquapin Oak:
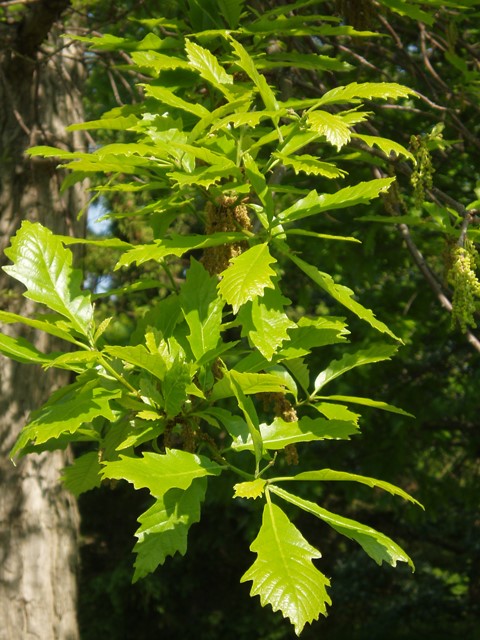
- Chinkapin oak’s common name is named because of the resemblance of the leaves to the Allegheny chinquapin
- Chinkapin oak’s scientific species name muehlenbergii honors an 18th and 19th century
Pennsylvania minister and botanist, Gotthlif Mühlenberg. - Historically the wood was used to fuel the
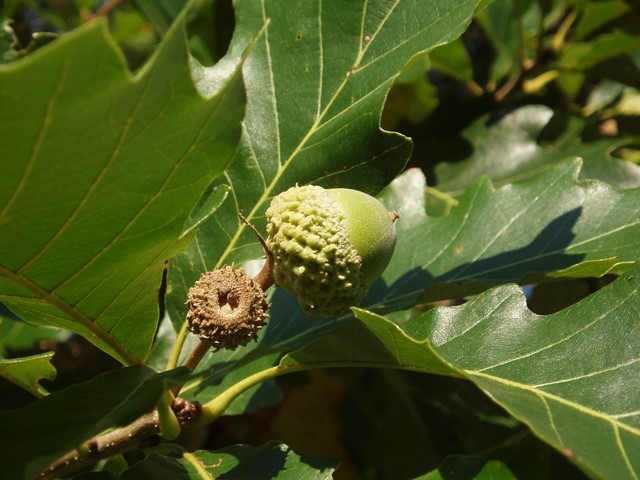
steamboats on the Ohio River. Now, it’s wood is durable and often used for construction and fence lumber - When roasted the chinkapin oak acorns are
sweet and edible. They were an important food
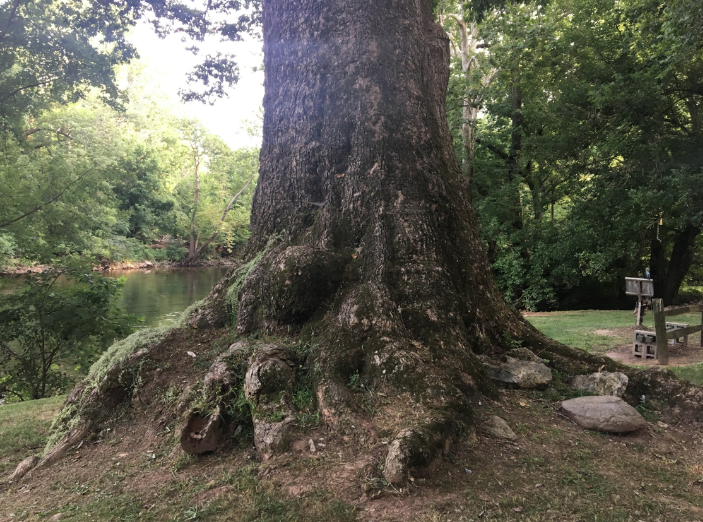
source for Native Americans. - As of 2020, the National Champion chinkapin
oak was 66 feet tall and 278 inches in circumference. It is located in Rockingham, Virginia.
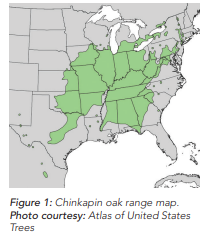











Sources
“Chinkapin Oak – Grow Native!” Grow Native!, 25 Oct. 2024, grownative.org/native_plants/chinkapin-oak/. Accessed 16 Nov. 2024.
Rawlins, Karan. Figure 3: Chinkapin Oak Seedlings Start out with Some Shade Tolerance, but Gradually Become Intolerant. Photo Courtesy.
“Texas Tree Selector: Tree Description.” Tamu.edu, Texas A&M Forest Service, 2024, texastreeplanting.tamu.edu/Display_Onetree.aspx?tid=82. Accessed 16 Nov. 2024.
Wiseman, Eric. “Tree Information- va Big Trees.” Vt.edu, 2018, bigtree.cnre.vt.edu/detail.cfm?AutofieldforPrimaryKey=176. Accessed 16 Nov. 2024.
